Types of Risk Factors
An Estimated
30 MILLION AMERICANS
suffer from some type of PN
Most Prevalent Types of Peripheral Neuropathy
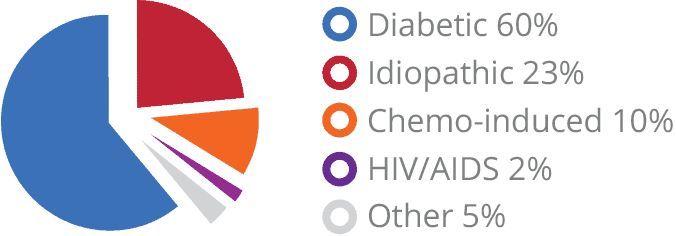
Between 60-70% of those with diabetes have PN.
- Nearly 54,000 diabetics have amputations each year
- More shocking is the fact that 75% of amputations are preventable
- The estimated annual cost to treat diabetes related chronic complications such as DPN is $58 Billion
30-40% of cancer patients are affected by PN.
30-40% of all cancer patients have Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). CIPN is caused by chemotherapy drugs used in cancer treatments. Chemotherapy is hardest on the nervous system due to the fact the nerve cells are more sensitive than other cells. Sensory nerves are at an increased risk to chemotherapy-associated damage compared to motor nerves.
The onsets and resolution of symptoms is variable. Some drugs may cause symptoms during or immediately after the first dose and some have a delayed onset of symptoms, up to several weeks, months, or even years, after the last dose.
23% of patients have PN of unknown origin.
Idiopathic peripheral neuropathy has no identifiable known cause and therefore is considered the primary disease. If a cause is detected, then the neuropathy is secondary to that and not idiopathic.
Idiopathic peripheral neuropathies occur typically in middle-aged and elderly individuals. It’s estimated that 23% of all neuropathy patients are diagnosed with idiopathic neuropathy.
1/3 of HIV/AIDS suffer from PN.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or AIDS are often accompanied by the development of peripheral neuropathic conditions. Of all HIV/AIDs patients, 33% have PN.
Other Causes of PN:
Immune system disorders:
- Guillian-Barré syndrome & Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP)
Anyone can develop GBS; however, it is more common among older adults. The incidence of GBS increases with age, and people older than 50 years are at greatest risk for developing GBS. In the United States, for example, an estimated 3,000 to 6,000 people develop GBS each year on average. - Charcot-Marie-Tooth
Charcot-Marie Tooth disease is the most common inherited disorder that involves the peripheral nerves, affecting an estimated 150,000 people in the United States. It occurs in populations worldwide with a prevalence of about 1 in 2,500 individuals.
Other autoimmune disorders can include but not limited to:
Repetitive Stress
A job or hobby that puts stress on one nerve for long periods of time increases the chances for development of peripheral neuropathy. Playing certain sports or musical instruments and/or using vibrating power tools even crutches can put pressure on peripheral nerves and cause nerve irritation and damage.
Alcohol abuse
Excessive drinking of alcohol can affect the nervous system, causing numbness of the hands and feet.
Vitamin deficiency
A lack of certain vitamins, especially B-1 (thiamin) and B-12 makes peripheral neuropathy more likely. Pernicious anemia, which occurs when the body cannot absorb B-12 properly, often leads to peripheral neuropathy. Learn more about vitamin deficiency
Other health problems
Medical conditions, including certain types of kidney disease and liver disease, or those with family history of genetic diseases that produce peripheral neuropathic pain symptoms and conditions put an individual at risk of developing peripheral nerve damage. Learn more about other health problems
Toxic substances
Exposure to some toxic substances can make one susceptible to peripheral nerve damage. These substances include heavy metals, such as lead, mercury, arsenic and organic solvents; and certain medications, such as those used to treat cancer or AIDS.