Exercise + Physical Therapy For Neuropathy
Home Living Well Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle Exercise + Physical Therapy For Neuropathy
Research has shown that strengthening exercises for peripheral neuropathy moderately improve muscle strength in people with PN. In addition, exercises to help peripheral neuropathy, when done regularly, may reduce neuropathic pain and can help control blood sugar levels. A comprehensive physical activity routine includes four kinds of activities:
Refer to a physical or occupational therapist, or a healthcare provider, regarding an exercise program that’s right for you.
Physical therapy may be helpful in maintaining strength, mobility, and function regardless of the underlying cause of Peripheral Neuropathy (PN). Patients with diabetic neuropathy may also benefit from physical therapy, however, diabetic neuropathy patients must also tightly control their blood sugar levels to prevent major fluctuations.
The objectives of physical therapy include:
- Maintaining and improve functions via a range of motion – passive range of motion exercises consist of progressive stretching and self-stretches
- Strengthening muscles – this includes exercising against increasing resistance, use of weights, and isometric exercise
- Balance training provides stability and prevents falls
- Physical therapists can also recommend braces and/or splints to enhance balance and posture
- Splinting is often used in the treatment of compression mononeuropathies, such as carpal tunnel syndrome
Occupational therapy is instrumental in helping a patient cope with the functional, vocational, and social impact of peripheral neuropathy by:
- Improving sensory-motor skills
- Teaching the patient to avoid exposure to environmental or industrial toxins
- Teaching self-care activities
- Teaching the patient safety issues, (e.g., paying more attention to the terrain when walking since falling or tripping may pose a risk for patients with PN)
- Teaching the patient to pay attention to issues which involve automatic functions (e.g., learning how to change positions smoothly to avoid a sudden drop in blood pressure and the risk of falling)
Aerobic Exercise
Increases your heart rate, works your muscles, and raises your breathing rate. For most people, it’s best to aim for a total of about 30 minutes a day, between 3-5 days a week. If you haven’t been very active recently, you can start out with 5 or 10 minutes a day and work up to more time each week. Or split up your activity for the day — try a 10-minute walk after each meal.
Here are some examples of aerobic exercise:
- Take a brisk walk (outside or inside on a treadmill)
- Take a low-impact aerobics class
- Swim or do water aerobic exercises
- Stationary bicycle indoors
Flexibility Exercises
Flexibility exercises, also called stretching, help keep your joints flexible and reduce your chances of injury during other activities. Gentle stretching for 5 to 10 minutes helps your body warm up and get ready for aerobic activities such as walking or swimming. Here are some flexibility exercises you can do at home.
Check with your physician before beginning any exercise program.
Plantarfascia Stretch
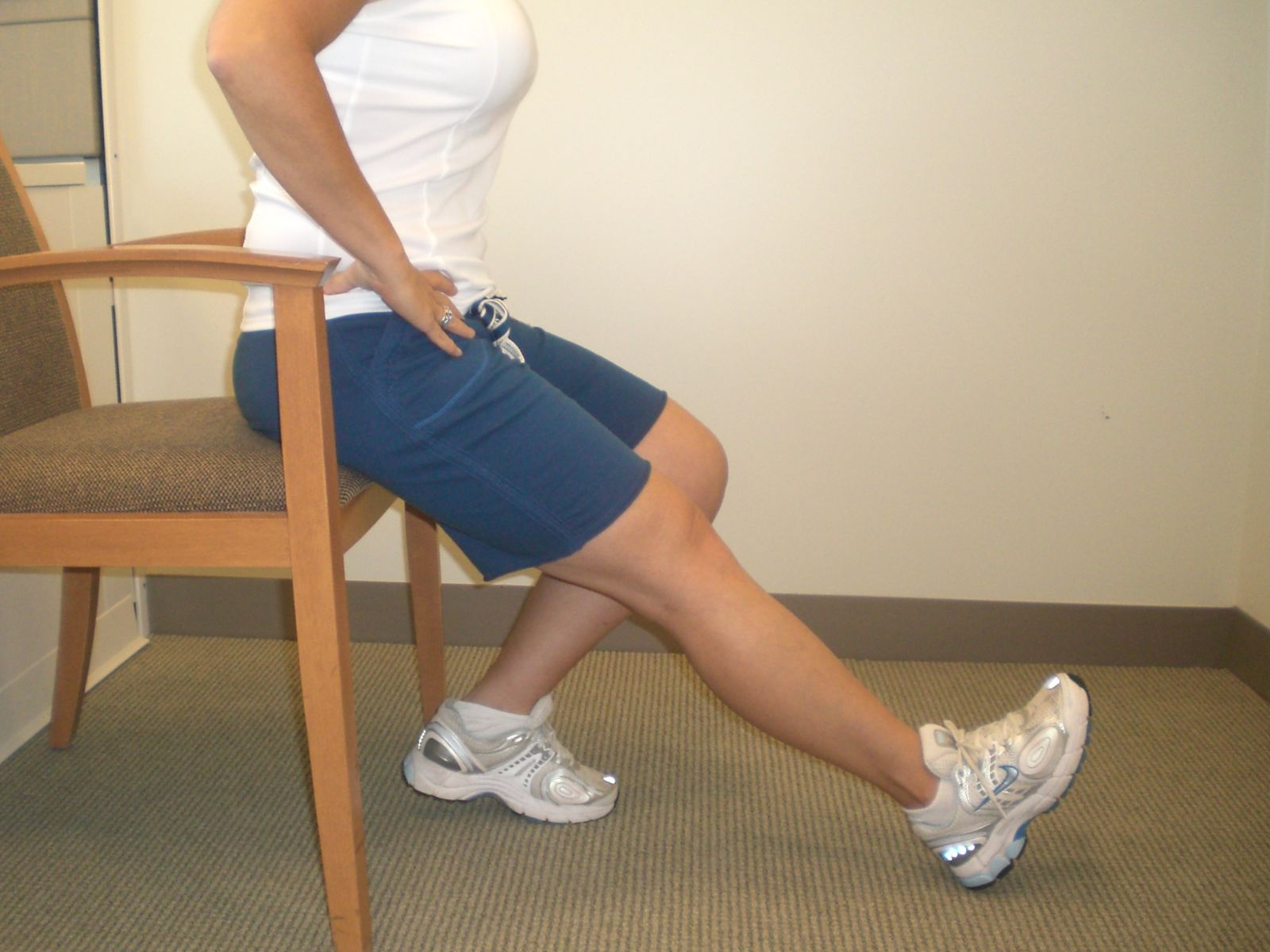

Seated Hamstring Stretch

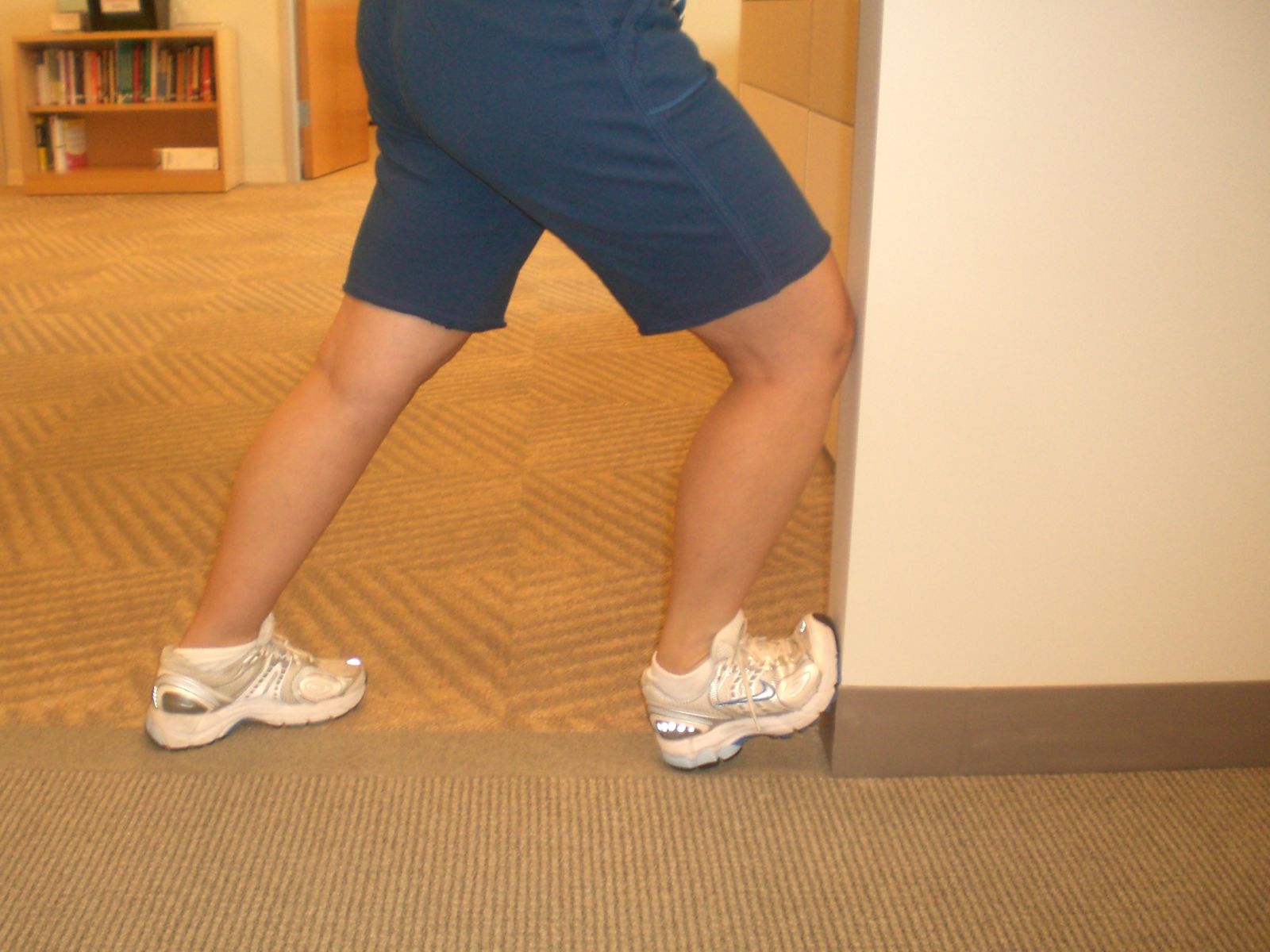
Calf Stretch
Strength Training
Strength training exercises help to make the muscles stronger and more injury resistant. It can help you regain lost strength in your muscles through constant training routines. Here are some strength training exercises you can do at home.
Check with your physician before beginning any exercise program.
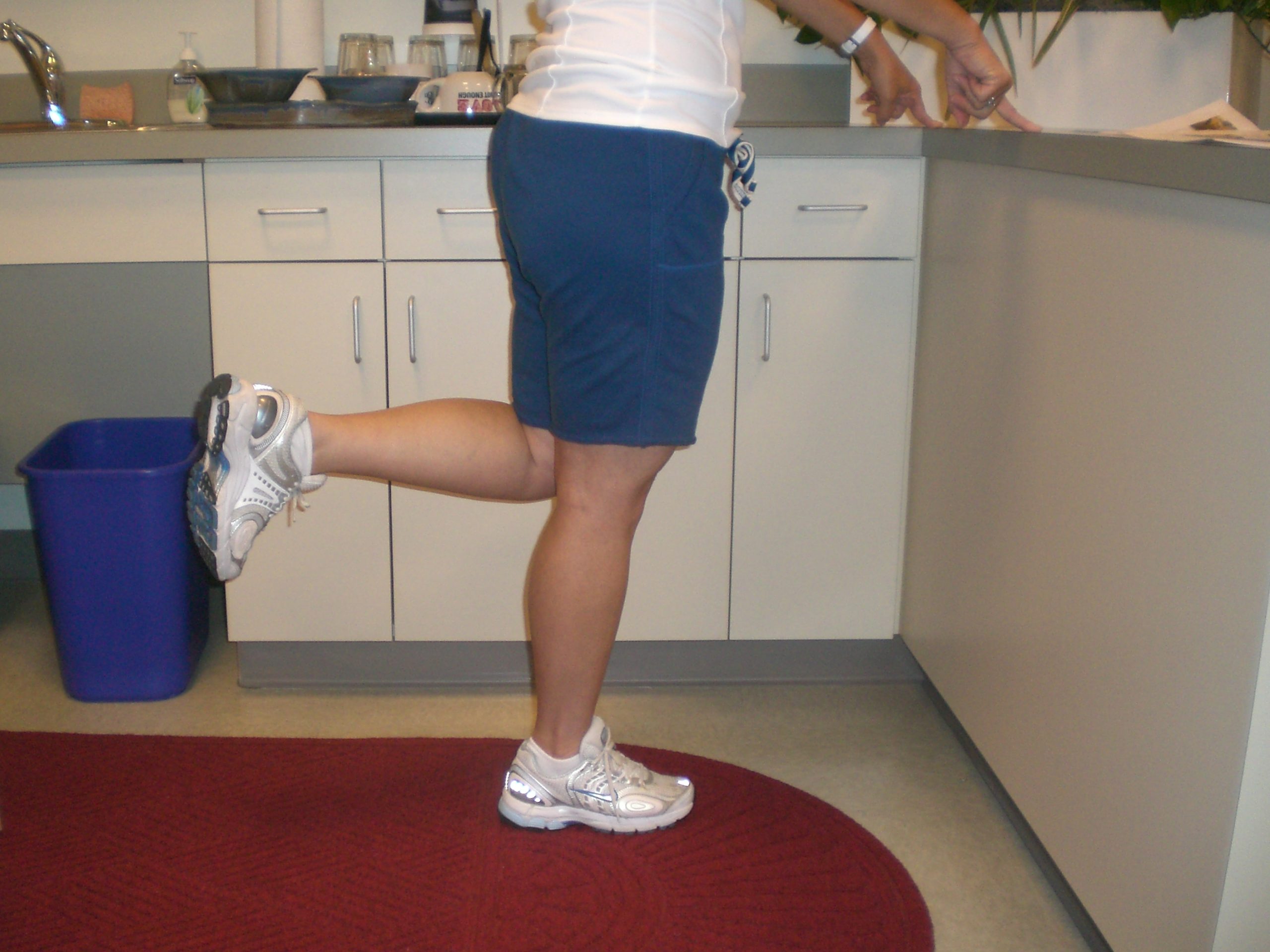
Kitchen Counter Calf Raises
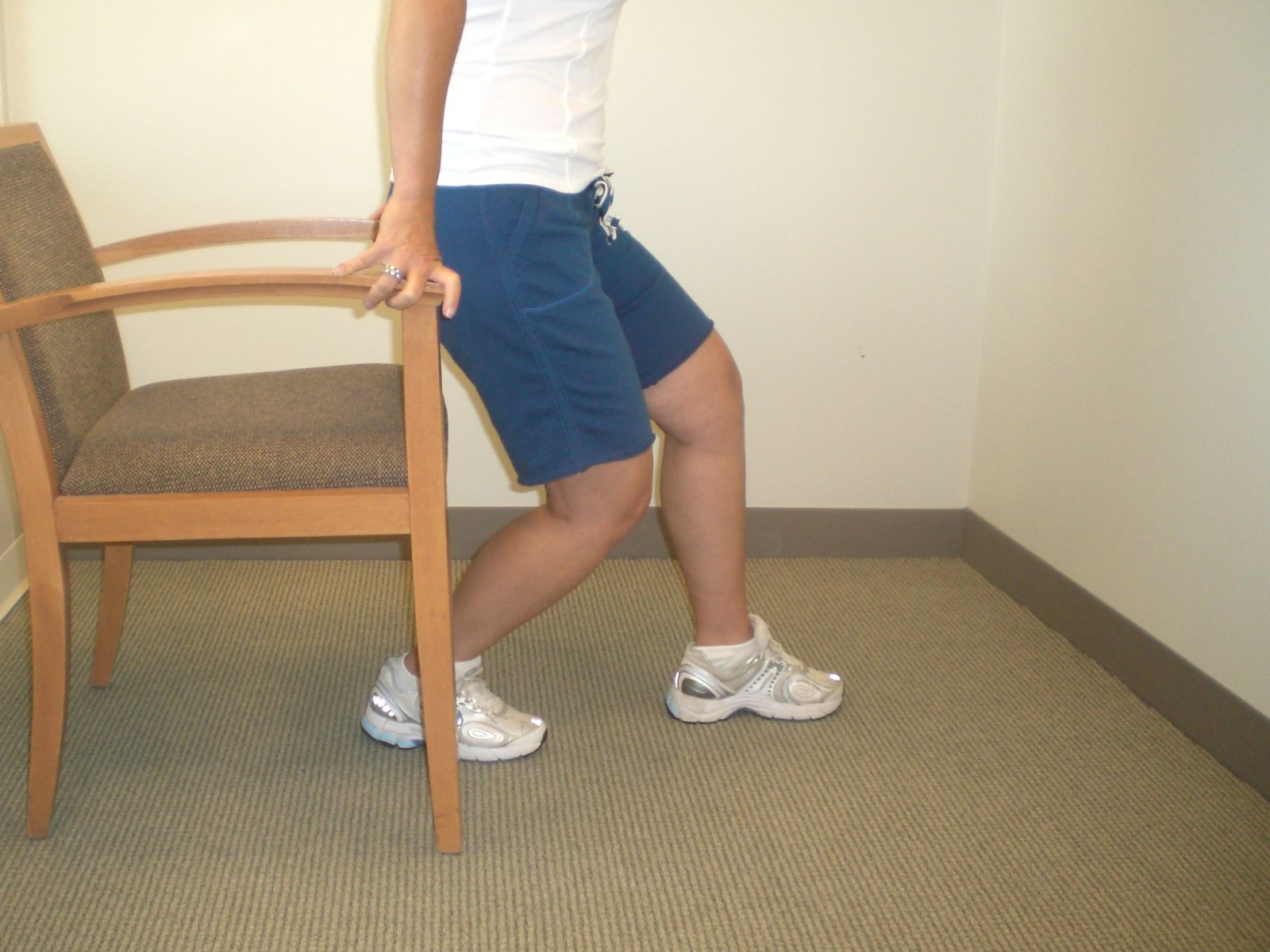
Chair Squat
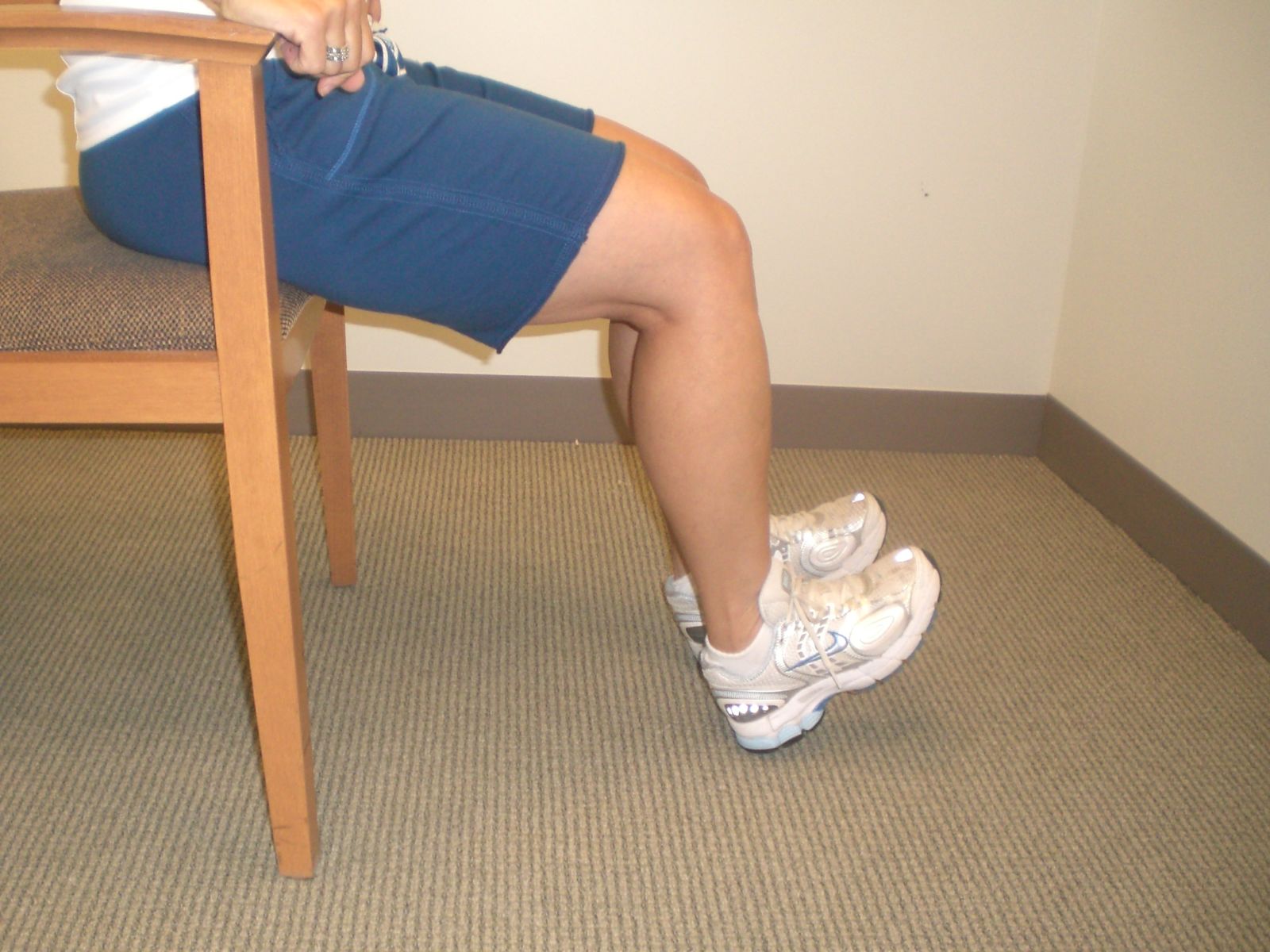
Seated Dorsiflexion
Balance
Keeping your balance system healthy is especially important if you have problems due to illness, such as joint pain, weakness or dizziness. Balance training can help you get back to normal, and overcome feelings of stiffness or unsteadiness. Balance, in particular, is emerging as an important element for the elderly. Older muscles are smaller and slower and respond less efficiently when you need to brace yourselves, making you more vulnerable to falls.

Kitchen Counter Calf Raises

Hip Flexion
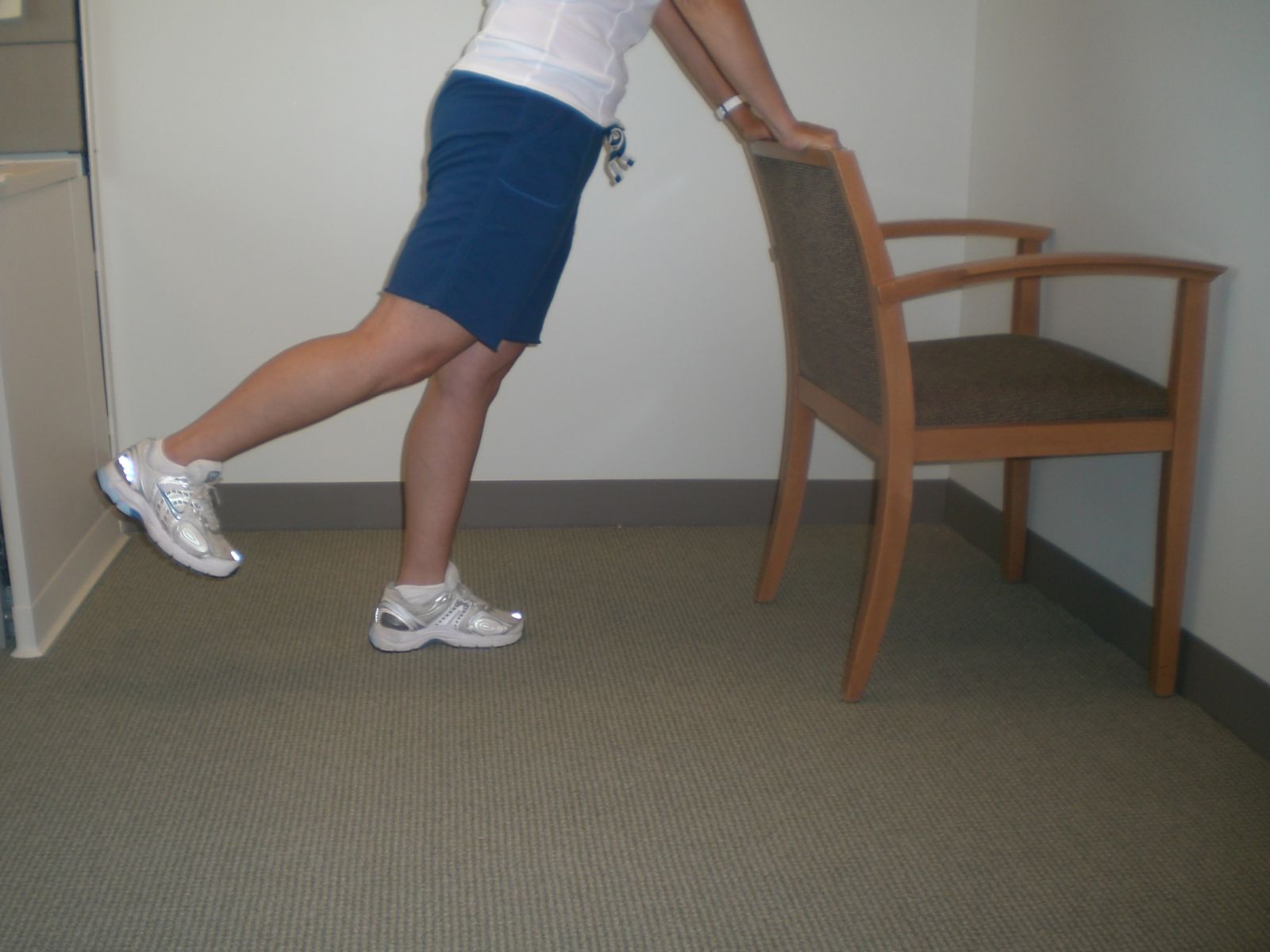

Hip Extension
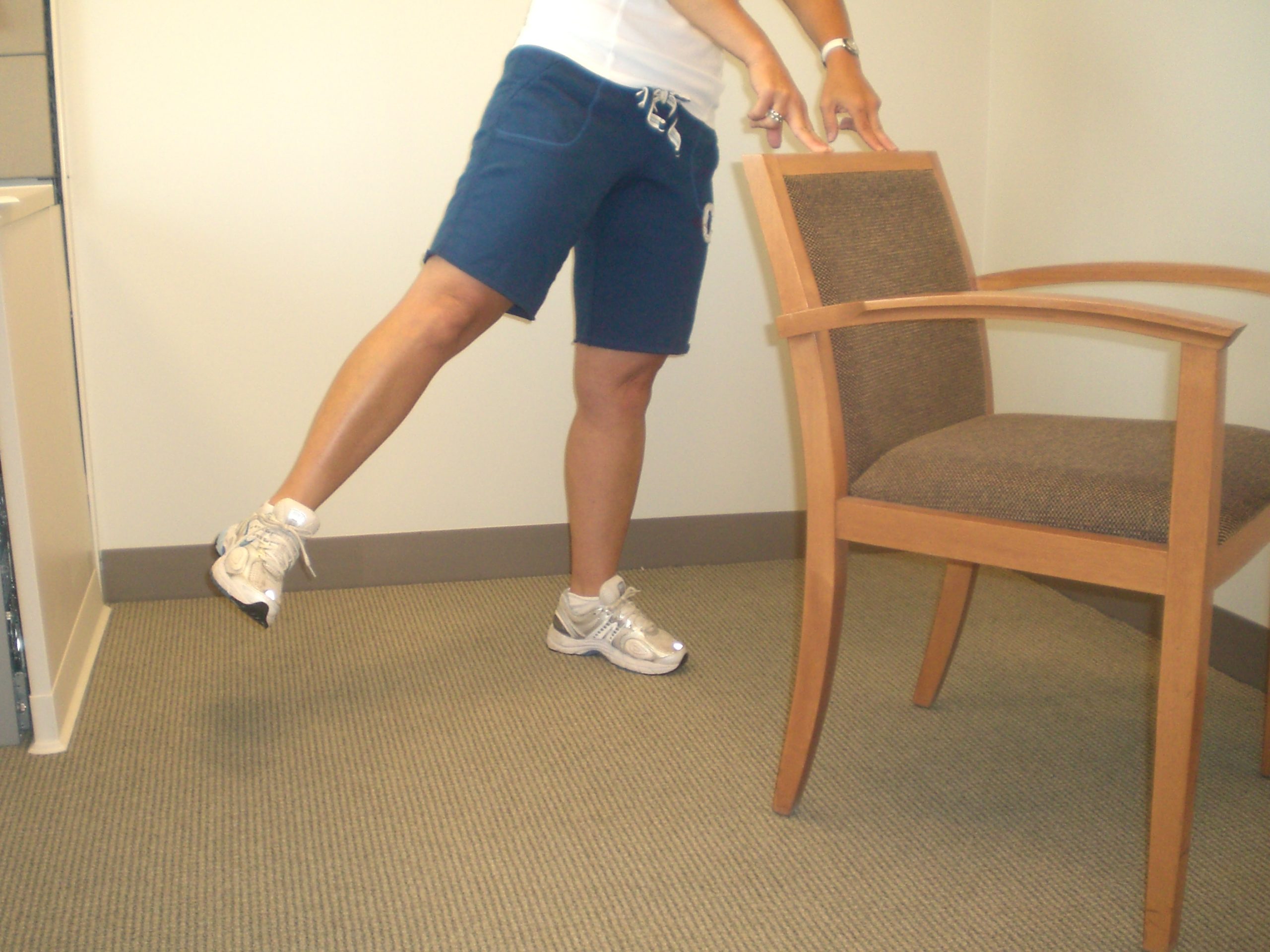
Side Leg Raise
See also...
Exercise for CIPN
Have you ever been watching TV and stumbled upon an advertisement promoting an 80s aerobics class—filled with bright workout outfits and groovy background music? For
How a PN patient maintains hope
Meet Jeff K., an FPN supporter and volunteer, recent retiree, and resident of West Hartford, CT Jeff K. was diagnosed with peripheral neuropathy (PN) nine
Helping PN Patients Directly
My name is Sumedha, and I am a current high school senior in Maryland. Though I do not have peripheral neuropathy (PN) and do not
Persistence
Sotirios from New Jersey shares his inspirational journey of SFN: from diagnosis to symptom management, showcasing persistence in the face of adversity. “Am I having
Coping with Chronic Pain
My name is Brooke Gottesman. I am a licensed clinical social worker (LCSW) working in mental health since 2004. I am currently in part-time private
Meet Margot Marsh
Margot Marsh has been through a lot over the years. She moved many times over her lifetime, mostly for other people. She has been married
Idiopathic Neuropathy: Q&A
Sometimes peripheral neuropathy seems to happen for no particular reason. Doctors call this disorder “idiopathic,” which means “of unknown cause.” Q&A with Norman Latov, MD,
Small Fiber Neuropathy: Q&A
Small fiber neuropathy (SFN) is a common, yet underappreciated, subclass of peripheral neuropathy. While SFN shares many features with large fiber neuropathy, it has unique
Dana’s Story: My Personal Journey with Small Fiber Neuropathy
I’m writing this essay for a couple of reasons: as a way to bring more awareness to small fiber neuropathy (SFN) and explain its toll
Anti-MAG Peripheral Neuropathy: Q&A
Anti-MAG peripheral neuropathy (Immunoglobulin M(IgM) Anti-Myelin Associated Glycoprotein Peripheral Neuropathy) is a rare autoimmune variety of peripheral neuropathy. In this type of PN, a person’s
Jen and Rosy’s Story: Two Moms Unite Over Small Fiber Neuropathy
Small Fiber Neuropathy brings two women together in friendship and for a cause Rosy George and Jen Roland were strangers living hundreds of miles apart.
Jeffrey’s Story: Life Is Good
“Optimism is the faith that leads to achievement; nothing can be done without hope.” —Helen Keller The Diagnosis I was diagnosed with idiopathic peripheral
Chuck’s Story: Exploring the National Parks
Chuck is a husband, father, grandfather, outdoorsman – and a PN patient who strongly supports the Foundation for Peripheral Neuropathy (FPN) and advocates for his own health and that of
Vicki’s Story: The Road to Fulfillment
Vicki’s Journey to Fulfillment: My name is Vicki, and I have bilateral progressive peripheral neuropathy. I have had this condition for over 15 years, and
FPN Welcomes the University of Michigan and Dr. Amro Stino
The Foundation for Peripheral Neuropathy (FPN) is pleased to welcome the University of Michigan as a new site for patient enrollments into the Peripheral Neuropathy
Diva’s Story: Self Help for Self Healing!
The Beginning To ring in the New Year four years ago, I fell off a horse. With all my other injuries, it took me a
Donn Seidholz’ Story: Staying in the Game
Donn Seidholz is a great storyteller – and he has great stories to tell. Donn shared stories about his time as a minor league baseball